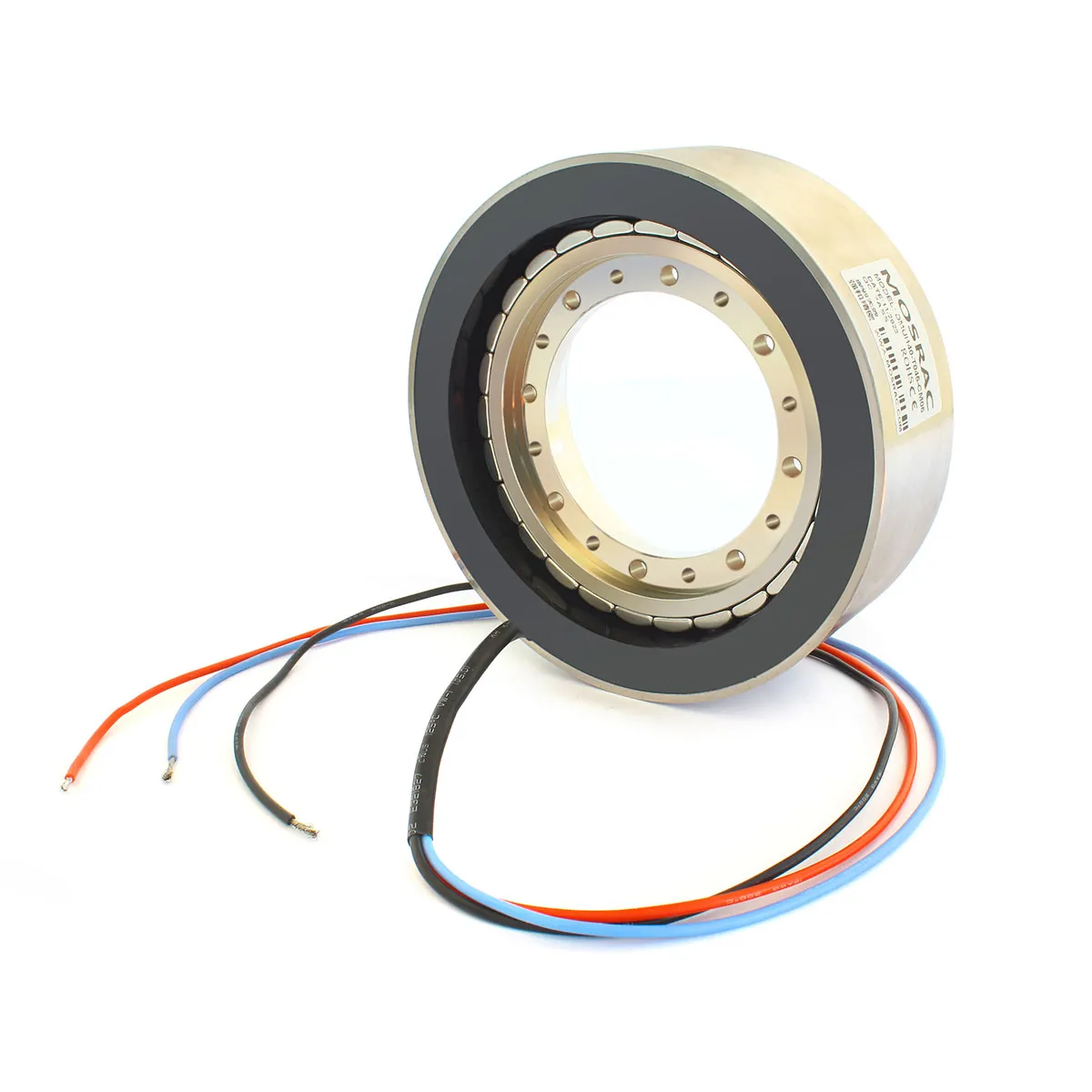
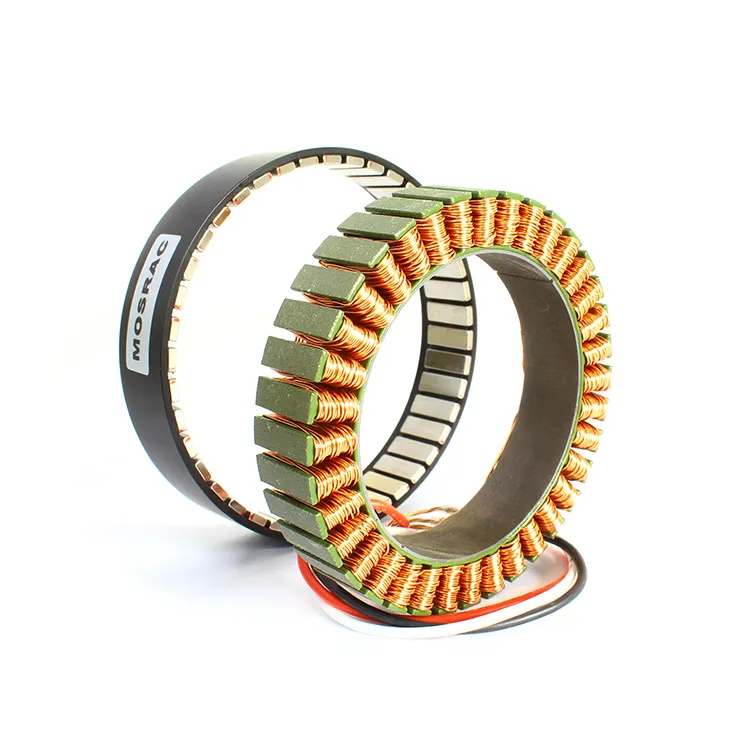
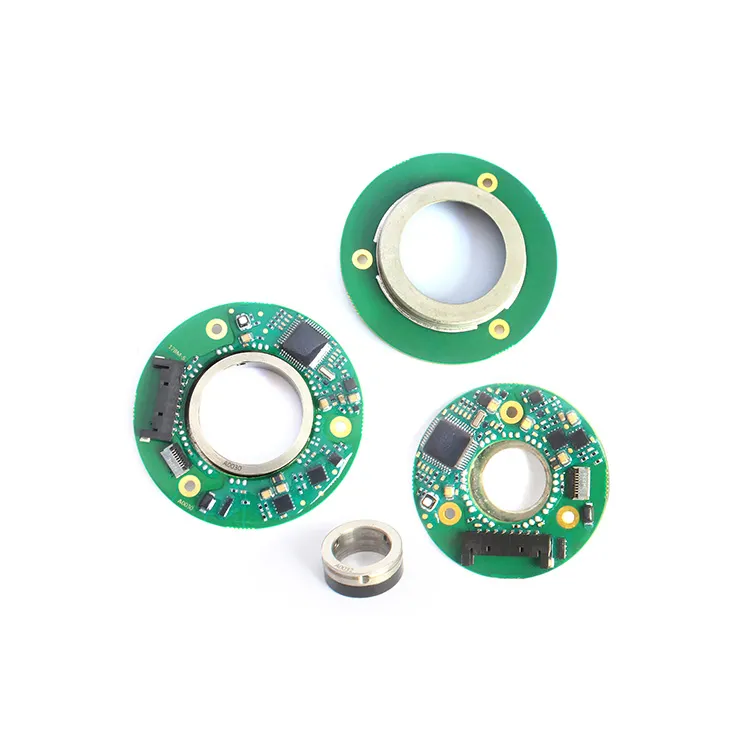
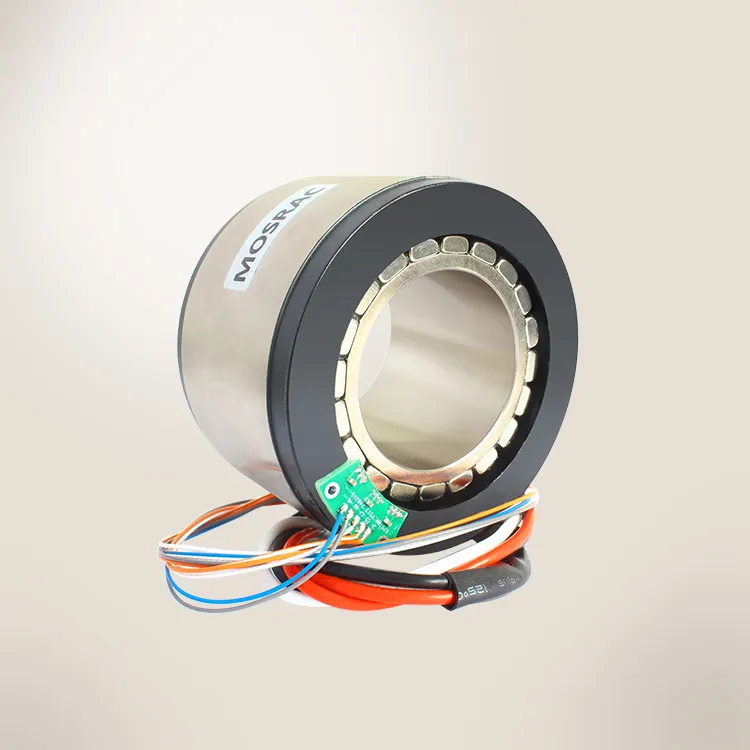
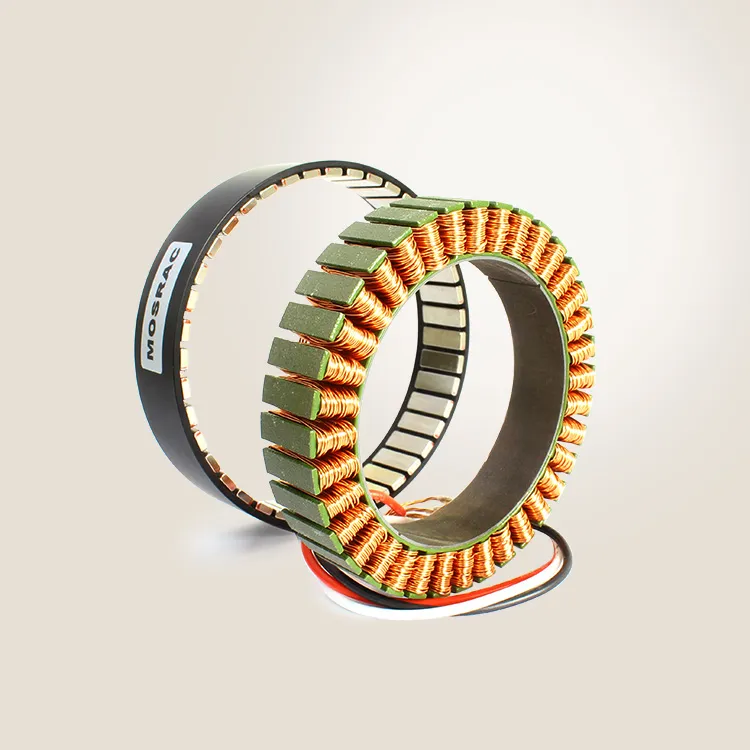
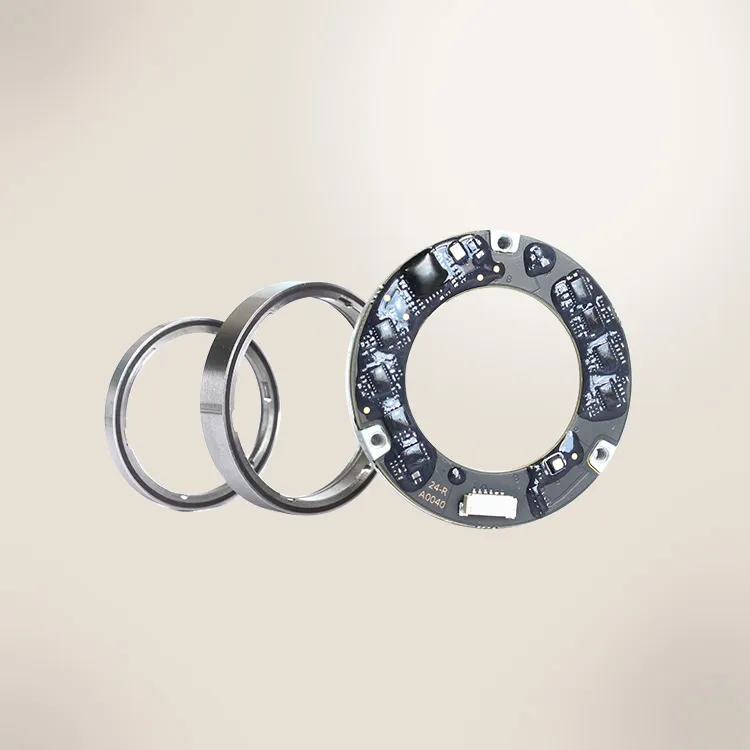
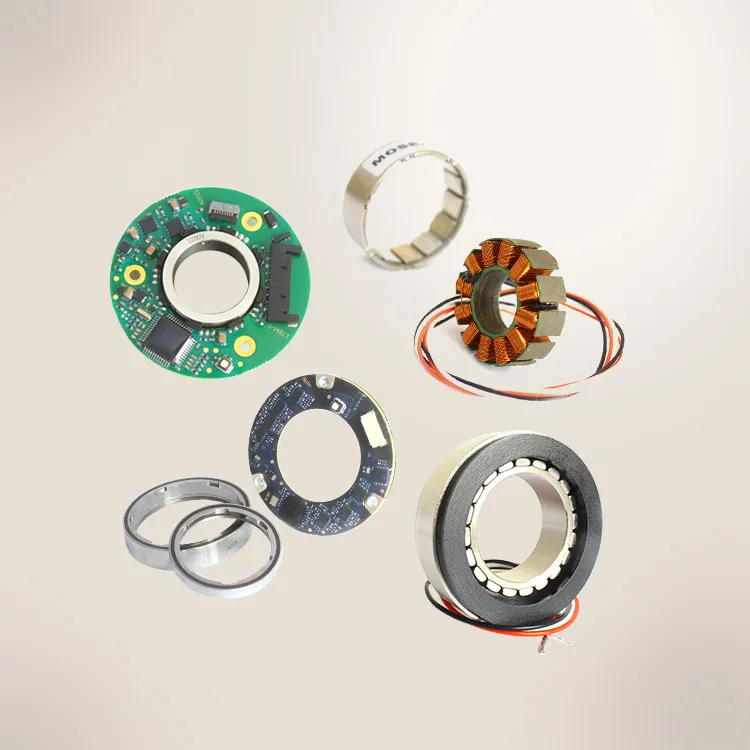
An encoder is a device that transforms data from one format to another for collaboration and processing effectiveness. It delivers a precise measurement of the present location of a shaft, axis, or other moving device. The speed of the movement can be determined by the control system through the analysis of the rate of change in the output signal of the encoder. Understanding the differences between the types of encoders is important for choosing the appropriate encoder for a specific task.
There are various types of encoders, such as rotary, linear, optical, and magnetic encoders. Each type of encoder has its distinctive benefits and is selected according to the specific requirements of the uses. There are some important technical specifications of encoders, such as resolution, accuracy, signal types, output configuration, input power, frequency response, and operating temperature.
MOSRAC can provide the best solution of encoder problems such as 17-bit high-resolution magnetic encoder as well as 24-bit high-resolution dual magnetic encoder.

In this article, we will discuss the different types of enoders with a basic understanding of their features and applications while highlighting the key considerations and important specifications of MOSRAC encoders for selecting the appropriate encoder for specific applications.
Most Commonly Used Types of Encoders
Some of the important factors that are used for the classification of encoders. The important factors are sensing technologies, encoder output, structure, and communication.
Ⅰ. Rotary Encoder:

Figure 1: Rotary Encoder
Definition:
Rotary encoders, also known as shaft encoders, are designed to measure the rotational location or angular motion of an object.
Types:
1. Incremental Rotary Encoder:
Incremental rotary encoders deliver relative angular location data through producing a series of pulses according to the rotation of the shaft.
2. Absolute Rotary Encoder:
Absolute rotary encoders deliver a particular location value for every shaft position, ensuring accurate and repeatable measures.
Features:
▪︎ Resolution: High
▪︎ Precision: Maximum
▪︎ Applications: Motor Feedback, Robotics, Automation
▪︎ Signal Output: Digital Pulses, Analog
▪︎ Atmospheric Sustainability: Indoor, Controlled Environments
Applications:
▪︎ Motor Feedback
▪︎ Robotics
▪︎ Automation
Ⅱ. Linear Encoder:

Figure 2: Linear Encoder
Definition:
A linear encoder is a sensor used to find out the displacement of an object in a linear order. It transforms linear replacement into electrical signals with preciseness and real-time feedback on the location of an object.
Types:
3. Optical Linear Encoder:
A photoelectric sensor is used in optical linear encoder to find out the linear displacement through the use of transparent and opaque scales on the measuring scale. Optical linear encoders show high resolution with high preciseness.
4. Magnetic Linear Encoder:
A magnetic sensor is used in a magnetic linear encoder to find out the linear displacement through the applications of magnetic signs on the scale. Magnetic sensors notice the modifications in the magnetic field with the movement of an object to measure displacement. Magnetic linear encoders generally have high durability and flexibility.
5. Capacitive Linear Encoder:
The modifications in capacitance are used in capacitive linear encoder to measure the displacement of an object. It has two parallel capacitive plates while one of those is permanent and the other one is attached to the moving object. The displacement of the object makes a change for the value of the capacitance, and the displacement is figured out through the measurement of the change of the value in capacitance value.
6. Inductive Linear Encoder:
Inductive linear encoder uses the principle of electromagnetic induction to measure displacement. The principle of electromagnetic induction is applied in inductive linear encoder to find out the displacement. It has a permanent coil and a coil attached to a running object. Once the object is run, the modifications in the electromagnetic field induction can be used to find out displacement.
Features:
▪︎ Resolution: High
▪︎ Accuracy: High
▪︎ Uses: CNC Machines, Precision Instruments
▪︎ Signal Output: Digital Pulses, Analog
▪︎ Atmospheric Sustainability: Indoor, Controlled Environments
Applications:
▪︎ CNC Machines
▪︎ Precision Measuring Instruments
▪︎ Automated Assembly Lines
▪︎ Printing Machines
Ⅲ.Optical Encoder:
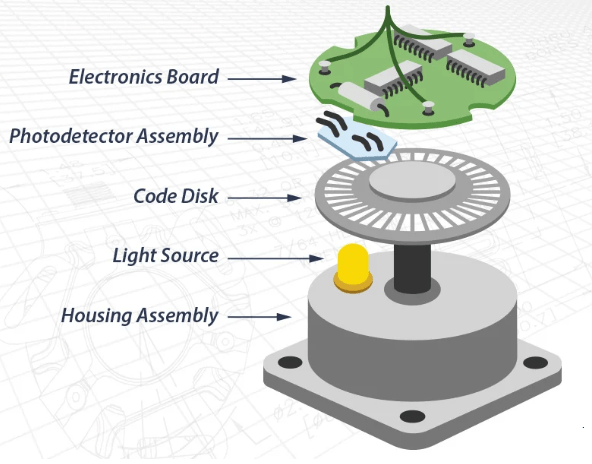
Figure 3: Optical Encoder
Definition:
An optical encoder is a motion-sensing device that uses light to transform mechanical motion into electrical signals. It gives precise location data in industrial applications.
Types:
7. Optical Rotary Encoder:
A stable and distinct order of light and dark is applied in an optical rotary encoder to select the location of an object. The most fundamental design of an optical rotary encoder is a mask encoder.
8. Optical Linear Encoder:
An optical encoder is a kind of device that can sense motion using light shone into a coded disk to trace the movement of a shaft. The encoder delivers feedback according to the interruption of light.
Features:
▪︎ Resolution: Very high
▪︎ Accuracy: Very High
▪︎ Uses: Semiconductor Manufacturing, Lab Equipment
▪︎ Signal Output: Digital Pulses, Analog
▪︎ Atmospheric Sustainability: Clean, Controlled Environments
Applications:
▪︎ Semiconductor Manufacturing
▪︎ Laboratory Equipment
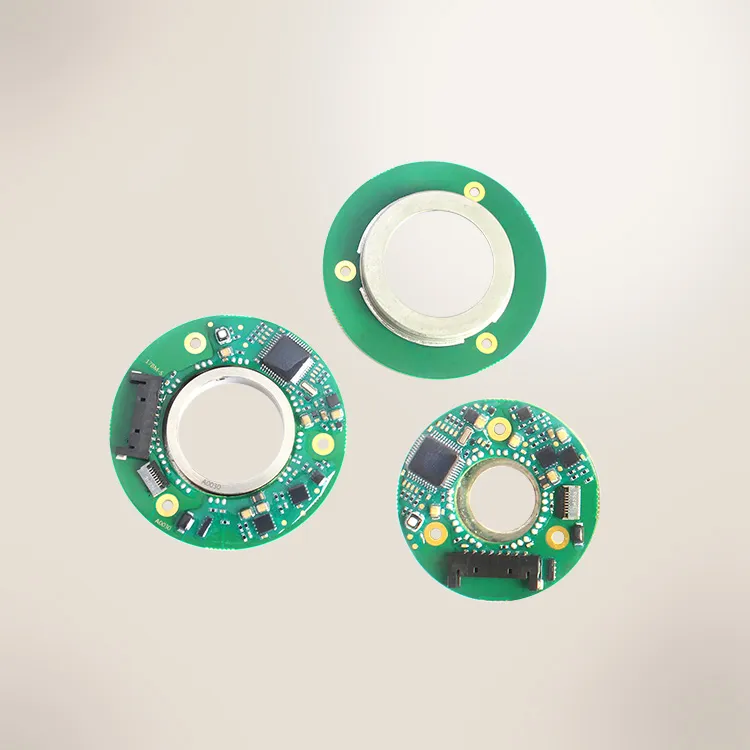
Ⅳ.Magnetic Encoder:
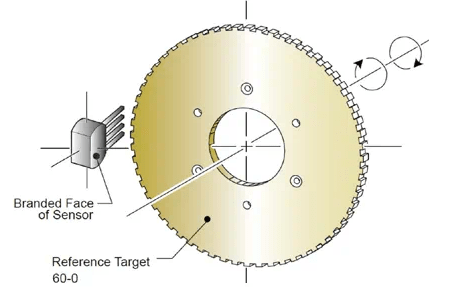
Figure 4: Magnetic Encoder
Definition:
The objective of the magnetic encoder is to find out the rotational location information with the changes of the magnetic field and transform them into electrical signals. A magnetic encoder has a fixed magnet and magnetic sensor. The magnetic encoder is designed to deliver stable digital feedback in a tough environment. It can be used in a wide temperature scale and can act as a high resistance to shock and vibration, and defense against defects. It possesses high accuracy of the output signal and simple installation.
Types:
9. Magnetic Rotary Encoder:
The magnetic field is used to determine the location in a magnetic rotary encoder.
10. Magnetic Linear Encoder:
The objective of a linear magnetic encoder is to be used as a sensor for measuring and regulating linear motion. It has a magnetic tape scale, and a reading head.
Features:
▪︎ Resolution: Medium
▪︎ Preciseness: Medium to High
▪︎ Uses: Automotive, Heavy Machinery, Outdoor Equipment
▪︎ Signal Output: Digital Pulses, Analog
▪︎ Atmospheric Sustainability: Harsh, Outdoor Environments
Applications:
▪︎ Automotive
▪︎ Heavy Machinery
▪︎ Outdoor Equipment
Other Encoders:
Ⅴ: Angle Encoder:

Figure 5: Absolute Angle Encoder
Definition:
The angle encoder is a measuring device with high resolution that can be used as a single-turn coil or multi-turn coil. It is a kind of rotary encoder. It is one of the most preferred types of encoders for industry use. It uses a disk or wheel that is connected to the shaft of a motor. An optical sensor can read the labels on the disk that can generate an electrical signal.
Types:
11. Incremental Angle Encoder:
An incremental encoder is a kind of encoder device that transforms angular location of a shaft into an analog or digital code to determine location or movement. It is one of the most widely used rotary encoders. It can find out the modification in load and can deliver displacement pulses.
12. Absolute Angle Encoder:
An absolute angle encoder can find out the modifications in the load. It can give the starting and final absolute locations of a load for high preciseness.
Applications:
▪︎ Motor Control
▪︎ Position Feedback
Ⅵ: Absolute Encoder:

Figure 6: Absolute Encoder
Definition:
The absolute encoder is very popular encoder in the industry due to its high accuracy. It provides exact location data of an object in the assembly line. Their high level of preciseness makes them popular in industries where safety is an important issue. If a power outage happens, the absolute encoder can be operated without recalibration.
Types:
13. Single-Turn Absolute Encoder:
A single-turn encoder can rotate 360 degrees and deliver an exact location within one full rotation. It can find out the modifications in location and can be used to trace the speed of a rotating shaft.
14. Multi-Turn Absolute Encoder:
A multi-turn encoder is able to rotate more than 360 degrees. It can keep the information of the number of full rotations of a shaft. It is popular for the applications of accurate positioning, such as CNC machines and 3D printers. It is a favorite encoder for the requirements of various measurements in long assembly lines.
Applications:
▪︎ CNC Machine Tools
▪︎ Robot Control
▪︎ Aerospace
What are the Main Considerations for Choosing an Appropriate Encoder
▪︎ Resolution and Accuracy: Encoders deliver higher resolution that makes them appropriate for control applications.
▪︎ Cost Issues: Encoders are usually expensive due to their higher precision, while magnetic and capacitive encoders can be cost-effective alternatives, especially in applications where a high level of accuracy is not important.
▪︎ Application Specifications: Different types of encoders possess different environments and operational conditions. Optical encoders are usual in clean environments, while magnetic or capacitive encoders are more robust in tough conditions.
▪︎ Stability and Reliability: Encoders may be more sensitive which make them appropriate for controlled environments. Magnetic and capacitive encoders are usually more robust and flexible in tough situations.
▪︎ Speed: Optical encoders are highly favored for high-speed applications due to their low latency. Magnetic or capacitive encoders are appropriate for low-speed applications.
▪︎ Size: Encoders are required to be compact and appropriate for uses with limited space.
▪︎ Integration Capacity: The chosen encoder type should be able to interface with motion control system and should deliver the necessary feedback for closed-loop control.
▪︎ Maintenance Issues: The maintenance issues of encoders should be into consideration due to their sensitivity to contaminants.
View Our Top Absolute Encoders:
1)S-series Magnetic Encoder:
Features:
▪︎ Ultra-thin Absolute Encoder
▪︎ Multiple output formats
▪︎ Strong anti-electromagnetic interference capacities
▪︎ 17-bit high resolution
▪︎ ±0.05° accuracy
▪︎ Arbitrary Hollow
▪︎ Different Sizes
Applications:
▪︎ High output accuracy
▪︎ Limited space.
2)T-series Magnetic Dual Encoder:
Features:
▪︎ Mosrac motor pattern magnetic technology
▪︎ Photoelectric-like resolution
▪︎ High resistance to environmental interference
▪︎ 24-bit high resolution
▪︎ ±0.01° accuracy
Applications:
▪︎ Robot-integrated joints
Looking for a custom solution?
Tell us about your requirements and our application engineers will help you find the right solution today!
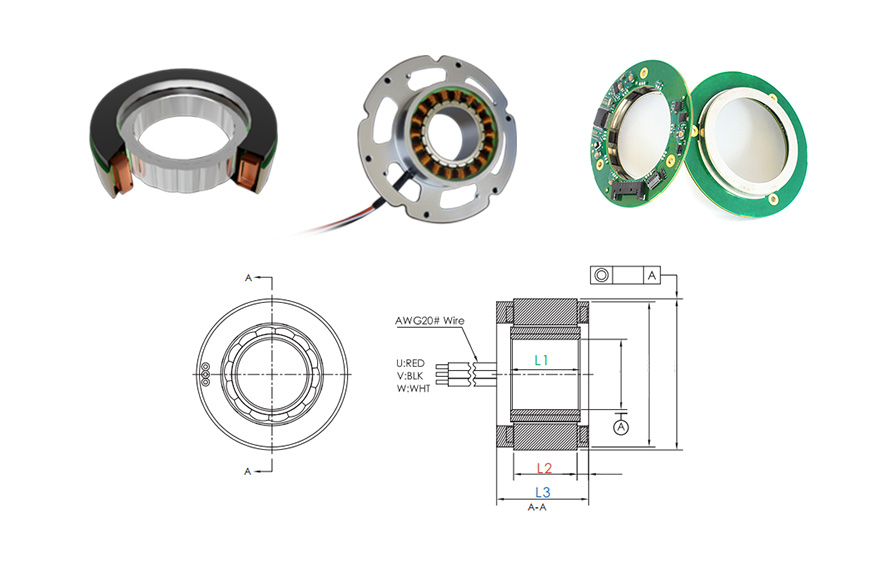
Conclusion:
Encoders are essential components in advanced technology, performing a crucial role in different types of industries. They deliver accurate feedback on location, speed, and movement for precise control and automation of systems.
Encoders improve efficiency, accuracy, and stability in industries like industrial automation, robotics, healthcare, and consumer electronics.
MOSRAC encoders can provide customers with optical, absolute, and electromagnetic rotary encoders for DC motors that will fit different types of applications. It can assist the customers in selecting the right encoder for use according to the requirements listed above. It provides customized encoder findings to satisfy specific requirements of customers.
Got a question about encoder types or our encoders? Contact me by email.