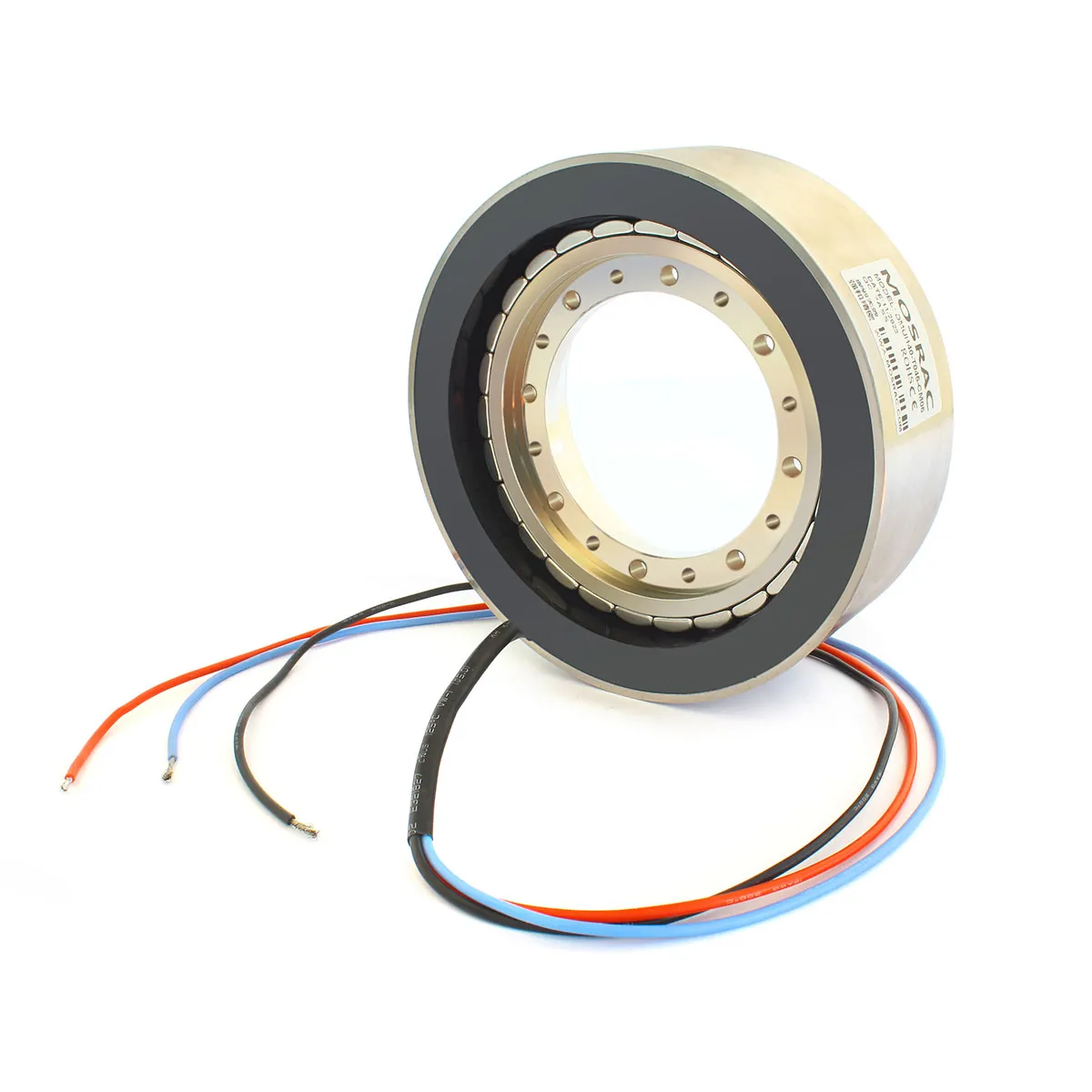
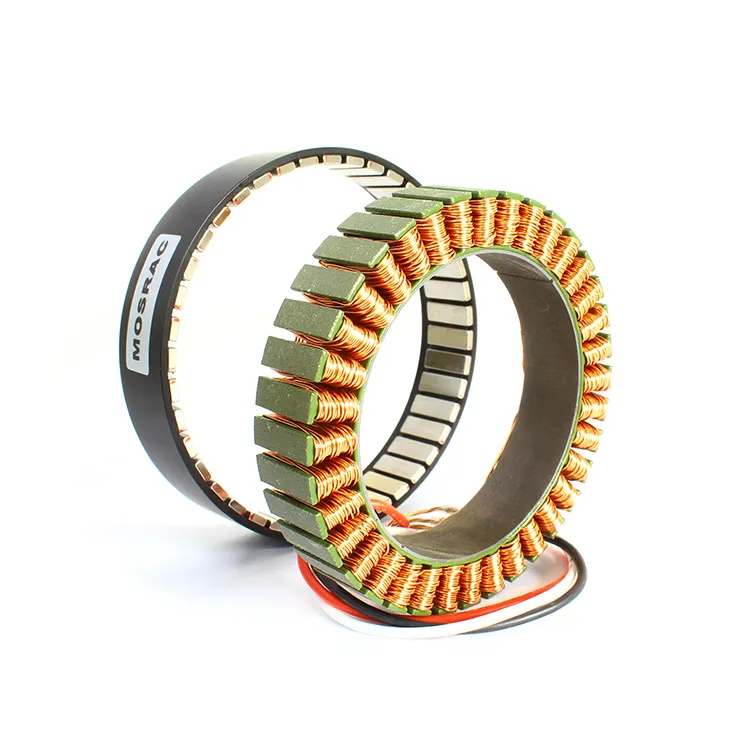
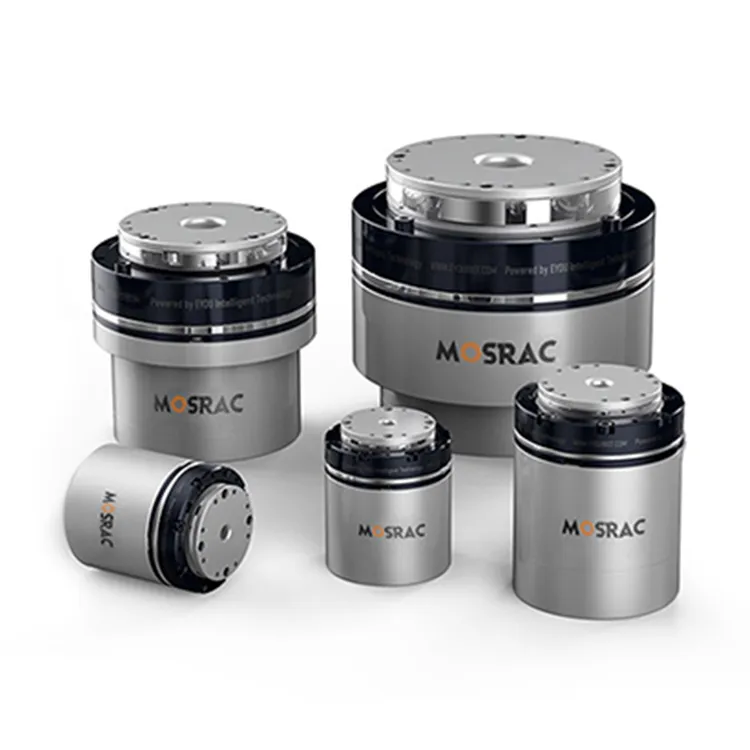
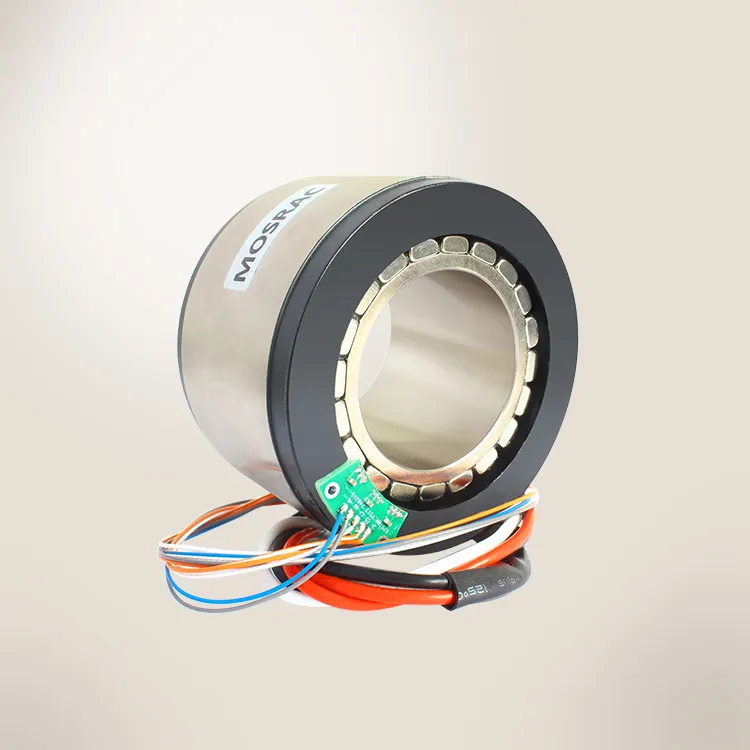
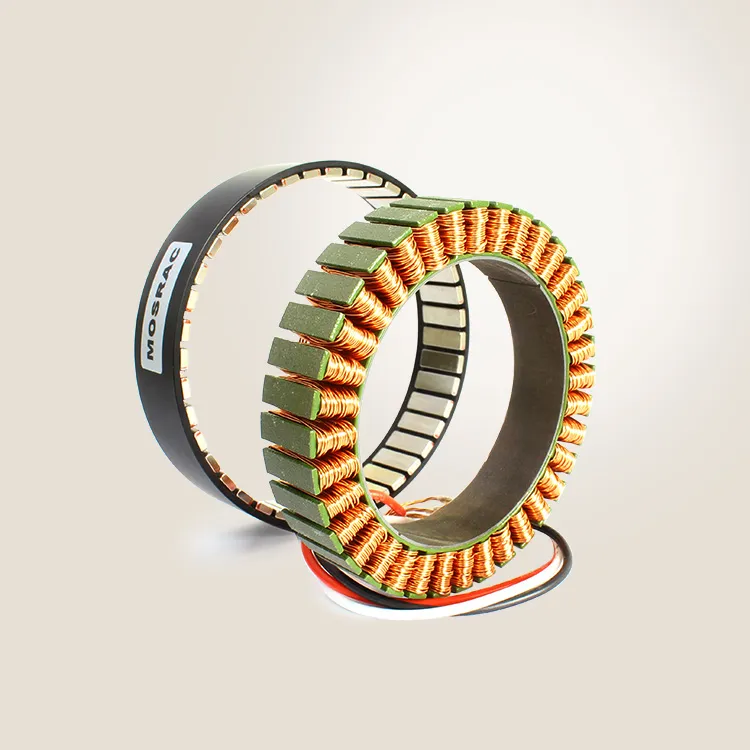
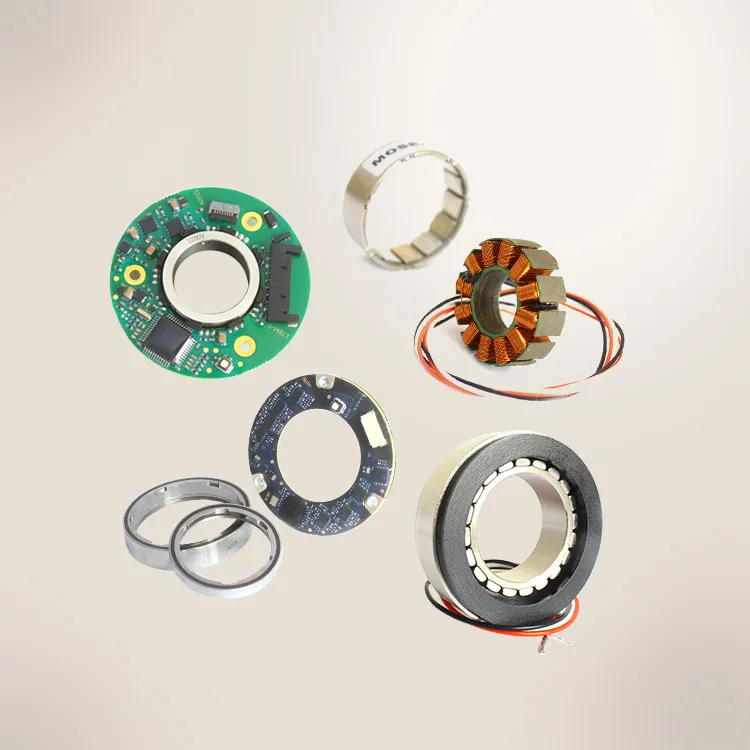
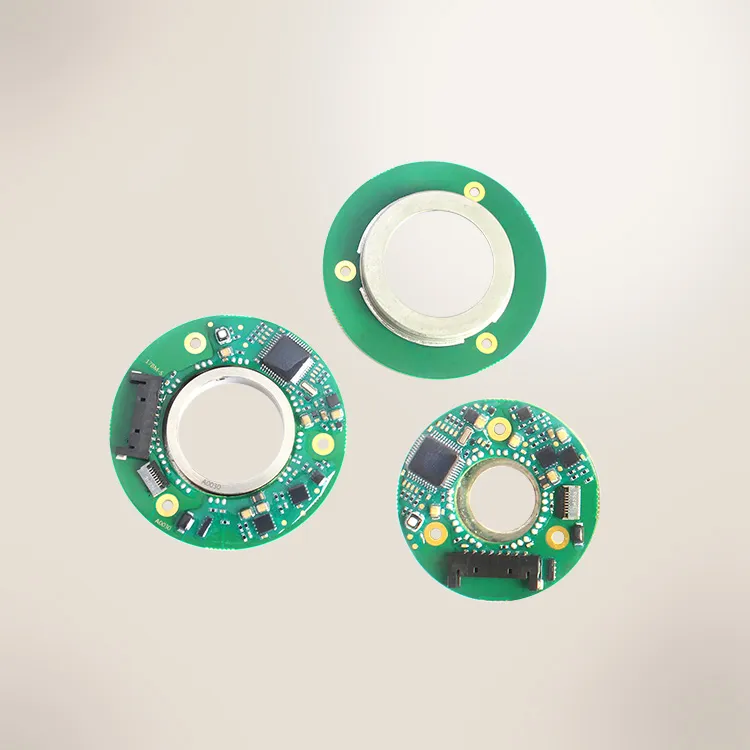
Mosrac Direct Drive Rotary Torque Motors
Torque is the amount of the rotational force applied to an object. It is an important measurement in the design, assessment, and operations of rotating objects. Torque motors, also known as direct-drive motors, are operated according to the principles of electromagnetism and show high power density, high torque, and exceptional dynamic response. They are rigid, more compact, low-cost with simple design and reduced maintenance.
The requirements of the users select the torque-producing capacity of motors. Each torque motor has its unique properties and is selected according to the specific requirements of the uses. There are various types of torque motors, such as low, high, constant, variable, torque-density, direct torque control motor etc. Some of the important technical parameters of torque motors are torque, speed, efficiency, and power.
MOSRAC torque motor technology is recognized as a leading solution for the requirements of high productivity, improved accuracy, increased dynamics of modern machinery. MOSRAC provides high-quality frameless direct drive torque motors with an outrunner design with excellent performance for various types of uses in industries. It delivers a very concise design, high accuracy, higher overload ability, high torque density, lightweight, and adaptability for industries
In this article, we will discuss the different types of torque motors with a basic understanding of their features and applications while highlighting the key considerations and important specifications of MOSRAC torque motors for selecting the appropriate torque motor for specific applications.
What are torque motors?
Understanding torque motors is crucial for different types of applications ranging from simple machines to sophisticated mechanical systems. A torque motor is a special kind of electric motor capable of generating a huge quantity of torque at comparatively low rotational speeds. Torque motors operate indefinitely at zero speed without overheating. This outstanding property makes them essential in uses that need a motor to keep a load stable for a long time.
Torque motors use the relation between a magnetic field and an electric current. It has two main components, such as a stator or stationary part and a rotor or rotating part. A magnetic field is generated by the stator while the rotor is rotated within the magnetic field. This rotation is transformed to mechanical systems, creating a torque that can generate work or create motion.
Torque motors are also known as "frameless" motors that mean they don't have housings, bearings, or feedback devices.
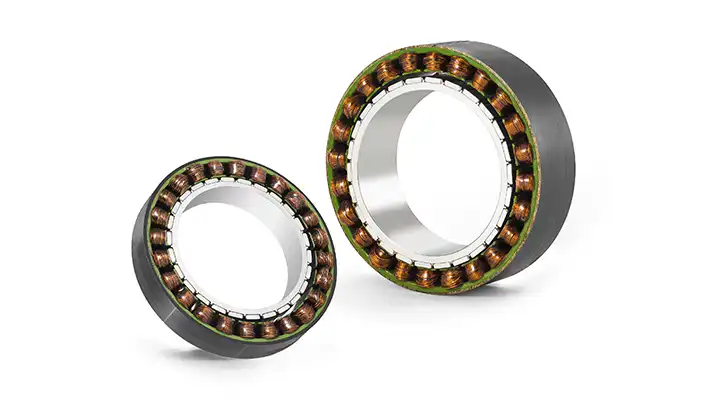

Mosrac Unpotted Frameless Torque Motors

Mosrac Potting Frameless Torque Motors
Key parameters:
▪︎ Torque is the maximum rotational force the motor can generate.
▪︎ Speed is the maximum rotation of the motor that is measured in revolutions per minute (rpm).
▪︎ Efficiency is the ratio of electrical energy transformed into mechanical energy.
▪︎ Power is the energy generation of the motor per unit time and expressed in Watts.
Key features of torque motor:
▪︎ High precision: Torque motors deliver high accuracy that is very crucial in the manufacturing and robotics industries.
▪︎ Low maintenance: Since there is no requirement of gearboxes or speed reducers, torque motors have fewer parts leading to lower maintenance costs.
▪︎ Simple integration: Easy integration with the advanced technology and application requirements has enabled torque motors to attain more torque, speed, sizes and variations and minimize heat.
▪︎ Large torque-speed scale: Torque motors provide high torque over a large scale of speed. The performance of a torque motor within its speed is shown in the following torque-speed curve.
▪︎ Dynamic performance: Dynamic performance can be improved a lot through a high control loop bandwidth. The applications of torque motors have a large scale of dynamic performance requirements. The peak torque or continuous torque will help the selection of a motor according to the specifications of a system’s duty cycle.
▪︎ High torque density: Torque motors need high speed to create high torque that has the negative impact of reducing preciseness and increasing wear and tear. The magnetic energy in a torque motor generates high torque at very low speed.
▪︎ Efficiency: High torque motors are usually more effective than standard motors under heavy load conditions due to their design and operational principles.
Fundamentals of torque motor:
Motors are often classified according to their torque-generating capacity, applications and types of motor involved. The classifications of motors have been discussed below:
Types:
Torque Range:
1) Low-Torque Motors:
Low-Torque Motors do not need high power for the applications, such as small appliances, toys, small pumps and fans.
2) Medium-Torque Motors:
Medium-Torque Motors are appropriate for conveyors, ordinary machineries, and automotive uses.
3) High-Torque Motors:
High-Torque motors are used in high-load uses like industrial machineries, electric vehicles, and lifts.
Torque Characteristics:
4) Constant Torque Motors:
Constant torque motors can preserve a fixed torque across a scale of speeds. This type of torque is very essential for the uses where the load is constant with speed.
5) Variable Torque Motors:
In variable torque motors, the torque varies with the speed. They are usually used in fans and pumps.
6) Torque Density Motors:
Torque-Density Motors generate a high amount of torque with respect to their size and are generally used in aerospace applications where space is limited but high torque is needed.
Starting Torque:
7) High Starting Torque Motors:
High Starting Torque Motors can generate a high amount of torque at the beginning to maintain a heavy load. These types of torque motors are found in compressors or crushers.
8) Low Starting Torque Motors:
Low Starting Torque Motors are used for the applications where the load is light.
Control Method:
9) Direct Torque Control (DTC):
Direct Torque Control motors are appropriate for accurate adjustment of torque and speed and used in advanced AC motor drives.
10) Vector Control:
Vector control motors are usually less accurate and similar to Direct Torque Control motors. It is used for different types of uses, such as CNC machines and conveyor belts.
Motor Type:
11) DC Motors:
DC motors usually provide a high starting torque, but they need more maintenance.
12) AC Induction Motors:
AC Induction Motors usually have a lower starting torque. These are more dynamic and need less maintenance.
13) Brushless DC Motor:
Brushless DC Motors provide high efficiency and high torque in a compressed size and are usually more costly.
14) Stepper Motors:
Stepper Motors deliver accurate control of location and speed, but do not provide high torque.
15) Servo Motors:
Servo Motors contain accurate control and high torque-to-inertia ratio. These are usually used in robotics and CNC machinery.
Motor Torque Calculation:
Torque in Newton meters can be found from the following fundamental principle:
T = ω/P
The motor speed needs to be converted from revolutions per minute (RPM) to radians per second according to the conversion factor ω = RPM × (2π/60).
As an example, if the output power of a motor is 200 watts and the motor operates at 2000 RPM, then ω=2000×(2π/60)=209.33 rad/s
The torque will be T=200/314.16=0.955 Nm
Torque-Speed Relationship:
Since the rated output power of a motor is a constant value, the torque and speed relationship is inversely proportional. If the output speed is increased, the output torque is decreased proportionally. If the output torque gets increased, the output speed gets decreased proportionally.
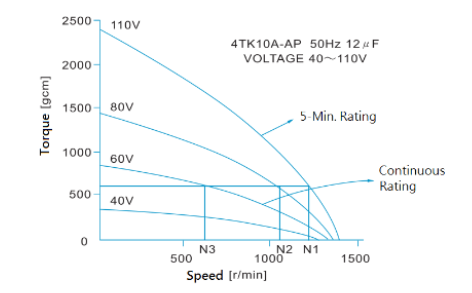
Figure 2: Torque-Speed Characteristics of a Torque Motor
Advantages of Torque Motor:
Strong Start-up and Acceleration: High-torque motors are crucial for the systems that need a strong primary force for the movement from a stationary location since they can deliver the required start-up torque.
Maintaining Heavy Loads: High torque motors are appropriate for industrial machineries, electric vehicles and other uses where a high amount of force is required to maintain the loads.
Higher Control: High torque in motors at low speeds is important for better control in accurate applications, such as robotic arms or CNC machines.
Higher Efficiency: Due to their design and operational principles, high-torque motors are often more efficient than standard motors, particularly under heavy load conditions.
Minimized Gear Requirements: To simplify the design and reduce costs, the high torque output may minimize the requirements for additional gearing in some applications.
Compressed Design: High-Torque motors can be more concise than low-torque motors that would require other mechanisms to provide the same amount of work,
Adaptability: High-torque motors are usually more adaptable and can be applied in a large scale of uses from conveyors to mixers.
Reduced Noise, Vibration and Torque Ripple: Torque motors eliminate extra vibrations and torque ripple with less moving parts for efficiency and accuracy. They generate low noise for a nice shop-floor environment.
Applications:
▪︎ Robotics and Industrial Automation: High torque with accurate control at low speeds is required in robotics applications. Torque motors play a crucial role in the development of robotics technology to fulfill the requirements.
▪︎ Machine Tools and CNC: Torque motors are used in CNC machines to adjust the movement of rotating axes, turntables, dividers and cutting tools accurately. To ensure precise machining of metal elements and different materials, torque motors are used in lathes, milling machines, and other machine tools.
▪︎ Material Transport: Torque motors are used in conveyor belts, cranes for maintaining the equipment effectively.
▪︎ Food processing and packaging machinery: Torque motors are used to maintain the movements of conveyor belts and turntables accurately in the food and packaging industry.
▪︎ Digital Printing: Torque motors are crucial to ensure higher dynamics and accurate location of conveyor belts for higher quality in digital printing.
Tips for Choosing the Right Torque Motor:
To select a torque motor for excellent system performance, some factors should be taken into consideration. These key selection factors have been discussed below:
▪︎ Motor Sizing: Torque motor sizing includes the torque and speed requirements for applications. Some factors like friction, torque, static force should be considered. The quantity of heat generated by motor power dissipation will select the temperature increase of the structure.
▪︎ Detent Outcomes: The production of iron-core torque motors with very low detent effects is an important factor. The design of a creative blend of open slots, ortho-cyclic winding and fractional pole pitch is used. This design minimizes detent effects substantially without any skewing of laminations or magnets.
▪︎ Motor Constant: The motor constant, Km, is a crucial parameter for the connection between torque and power losses. A torque motor with a higher value of Km can generate higher torque. The value of Km can be found from the design and structure of the motor.
▪︎ Thermal Issues: The thermal management is always an important issue for the performance of a torque motor. Torque motors generate heat during its operation. The heat needs to be removed to minimize the thermal expansion of the torque motor. Keeping the torque motor cool is essential for high accuracy. Torque motors can be cooled by free air convection or a liquid coolant.
View Our MOSRAC Torque Motor:
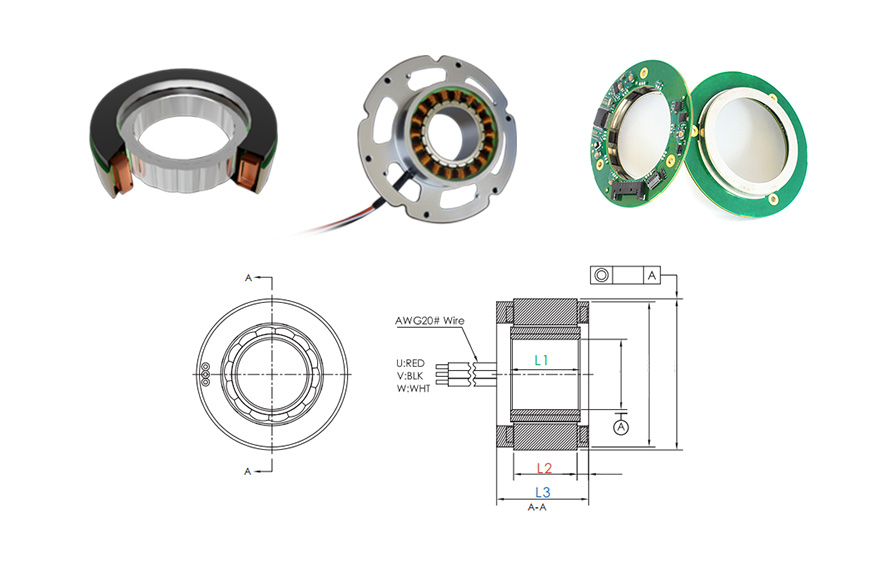
MOSRAC torque motor design including the integration of rotor and stator provides maximum flexibility, lightweight with compact size. It is appropriate for the uses where space is limited to fulfill the industry requirements. Excellent torque, speed, size and temperature for different uses can be attained by our frameless direct-drive torque motors. MOSRAC is prominent for its advancement of special and fully customized torque motors. MOSRAC torque motors contain industry-leading performance and are cost-effective.
Types:
Inrunner Frameless Torque Motor:
▪︎ Torque values: 0.025Nm to 50 Nm.
▪︎ Voltage Ranges: 24 V to 48 V or custom-oriented.
▪︎ Outer Diameters: 25 mm to 200 mm or custom-oriented.
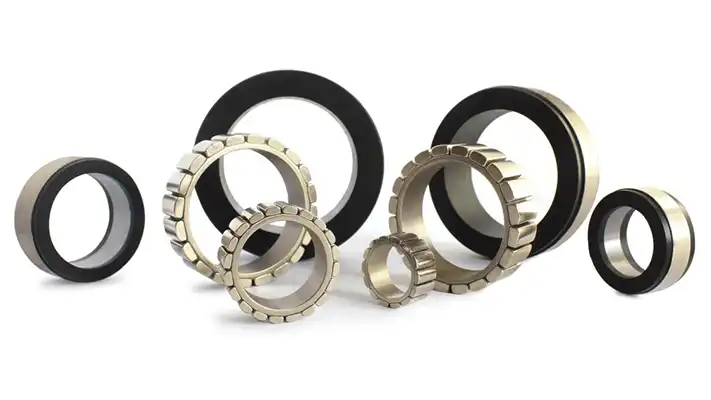

Mosrac Inrunner Frameless BLDC Torque Motors
Outrunner Frameless Torque Motor:
▪︎ Torque values: 0.01Nm to 6Nm
▪︎ Voltage Ranges: 12, 16, 24, 36 and up to 48 V or custom-oriented.
▪︎ Outer Diameters: 14.9mm (0 587"), 22mm (0.866”), 49mm (1.929") up to 485mm (4.291") or custom-oriented.
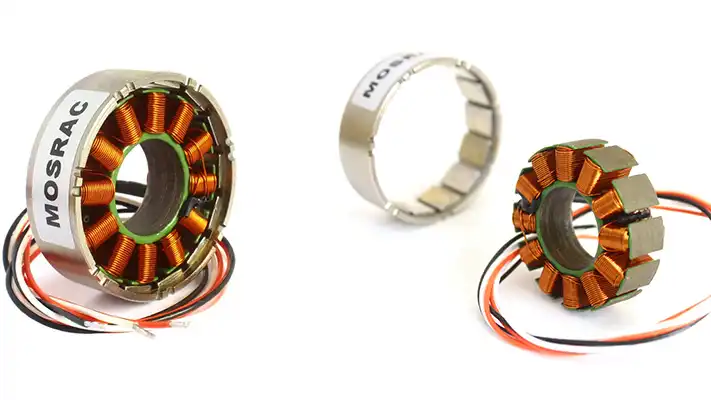

Mosrac Outrunner Frameless Direct Drive Torque Motors
Features:
▪︎ Integrated Thermal Sensor
▪︎ Various Sizes
▪︎ Low Weight
▪︎ Excellent Precision
▪︎ Very Compact Design
▪︎ High Efficiency
▪︎ Low Cogging
▪︎ High Torque Density
▪︎ Low Maintenance
Applications:
▪︎ Robotics
▪︎ Medical
▪︎ Aerospace
▪︎ Semiconductor
▪︎ LCD manufacturing equipment
▪︎ Industrial Automation
Looking for a custom solution?
Tell us about your requirements and our application engineers will help you find the right solution today!
Conclusion:
Due to their high torque at low speeds, excellent precision and low maintenance costs, torque motors have been an essential component in various industries. Torque motors have been an integral part of a wide range of applications from electric vehicles and industrial machinery to robotics and home appliances.
Torque motors generate the enhancement of efficiency, accuracy, and stability in modern technological industries. Although they face challenges of thermal management and size limitations, technological advancements are being continued to enhance their capabilities and applications.
MOSRAC torque motors deliver the customers with various types, compact design, high precision, higher overload capacity, high torque density, and lightweight that will be suitable for different applications in industries. MOSRAC is the best solution for torque motors. MOSRAC is ready to help the customers to choose the appropriate torque motor for different applications.
Any questions or comments about Frameless Motors, Direct Drive Rotary Motors, and Encoders? Contact us at sales12@mosrac.com for sales, technical inquiries, or order samples online today!