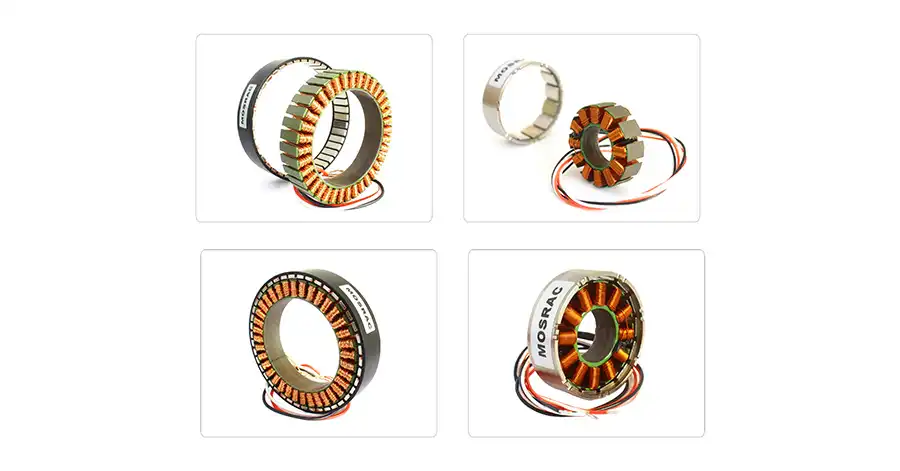
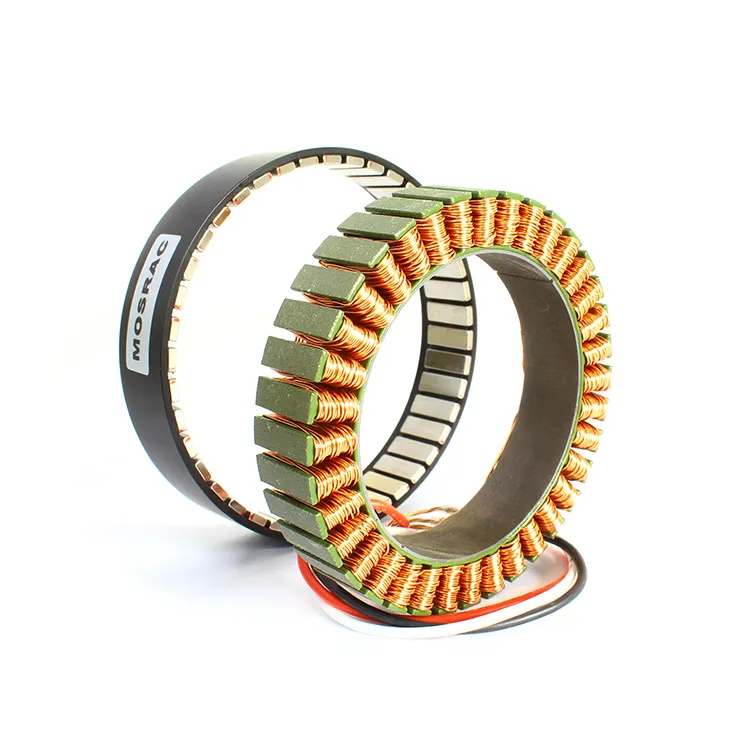
Customizing the Pole Count and Slot Count in a Torque Motor to Optimize Performance for a Specific Application
Motor torque and speed are dependent on motor pole count. So, it is crucial to determine the pole count to get an idea of the motor's performance. But how can you choose the pole count of a motor?
You can count motor poles using information like frequency, RPM, Kv, rating, etc. Also, polar counts can be detected by physical inspection.
Let's learn this process in detail step by step.
What is motor pole count?
Motor pole count gives the number of magnetic poles in an electric motor. The number of poles directly affects the speed and performance of the motors. Each magnet has a north and south pole. As the rotor rotates, it generates a fluctuating magnetic field.
This design affects the speed-torque characteristics of the motor. A higher pole count generally results in more torque at lower speeds. This motor is perfect for applications requiring precise control at various speeds.
Therefore, the motors with a specific pole count can make noise less and smoother when working.
Different types of motor pole count
The pole count of a motor significantly influences its performance, efficiency, and application suitability. Here, I will discuss the different types of motor pole counts:
a: 2- Pole motor
A 2 pole motor is equipped with two magnetic poles, making it ideal for high-speed applications. It consists of a north magnet and a south magnet. This straightforward design ensures smooth operation.
Motors with a two-pole configuration are generally useful in applications where they need high speed. Operating at 60 Hz, they can reach speeds of 3,600 revolutions per minute. It’s making them suitable for a variety of equipment, including fans, printers, and small appliances.
b: 4- Pole motor
In motors with 4 poles, the magnetic pole arrangement is effectively designed for a wide variety of applications. These motors maintain an impressive balance between torque and speed, operating at a synchronous speed of 1800 RPM. This feature makes them widely preferred in numerous industrial settings.
c: 5-Pole Motor
5 pole motors resonate with a wide range of applications. It rotates at 600 RPM, while it operates at a nominal frequency of 60 Hz.
5 pole motor is a powerful tool in industry, for work that requires high efficiency and reliability, such as fans, blowers, pumps, and other electrical equipment.
d: 6- Pole motor
The 6-pole motor, consisting of 3 north and 3 south magnets, is an attractive option for electric motors. Its unique feature of having 6 poles allows it to achieve low synchronous speed. It typically runs around 1200 RPM at a standard frequency of 60 Hz. This slow speed can benefit applications requiring high torque at low speeds.
e: 8- Pole motor
The 8-pole motor is distinguished by its unique design and performance, making it a significant alternative for slow magnetic field variations. It has a configuration of 4 north and 4 south magnets.
Although this motor provides increased torque, it operates at lower speeds, enabling improved precision and smoother operation. As a result, these motors are ideal for jobs that demand stable speed across varying loads, including robotics and industrial equipment.
f: 10- Pole Motor
The 10 pole motor features an arrangement of 5 north poles and 5 south poles. This configuration categorizes it as a 5 pole pair motor, allowing for efficiency and improved torque.
Typically, this type of motor operates at approximately 540 RPM when connected to a standard frequency of 50 Hz. This makes the 10 pole motor particularly useful in a range of industrial applications
g: 12- Pole Motor
The 12 pole motor, consisting of 6 north and 6 south magnets, is also considered a 6 pole pair motor. 12 pole motor typically runs around 600 RPM without load. This pole is suited for electric windows, windshield wipers, and fuel pumps.
Mosrac motor pole count
We provide a range of motor pole counts to meet different types of application needs. In our frameless series, you can choose from 7, 10, or 13 poles, ideal for designs and customizable applications.
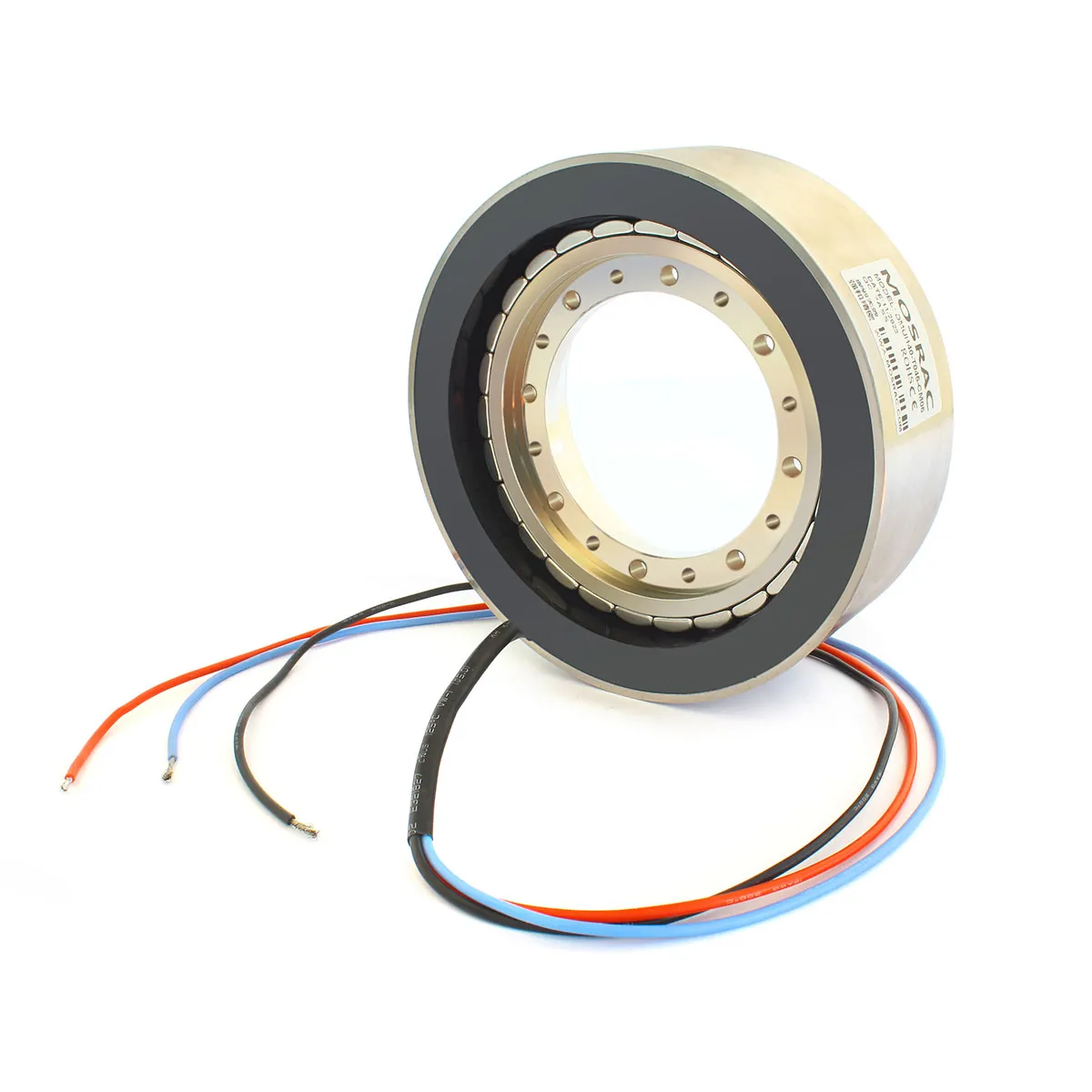
For those seeking housed direct drive solutions, we offer an extensive selection. Our housed DD series features multiple options with pole counts of 5, 7, 10, 11, 20, and custom pole count. This variety ensures you find the perfect fit for your specific requirements.

U25-Series 7 Pole Frameless Motor

U38 Series 7 Pole Frameless Motor

Click for more information on Mosrac's direct-drive frameless motor kits with different motor pole counts.
To explore our full range of motors and their specifications, visit our product collections now.
How to determine motor pole count?
It is very important to determine the motor pole count to understand the functionality of the motor. You can understand using some insightful methods.
Now, here I will discuss these methods:
1. Check the nameplate
The nameplate serves as a repository of information, especially when determining motor poles. It contains information such as voltage, current, RPM, and frequency, which are important for calculating poles.
2. Calculate using RPM
Have you wondered about calculating the number of poles? To calculate the number of poles, we need motor RPM and Max Hz. The equation is as follows:
Number of pole = (120 x Max Hz) /Max RPM
Here,
RPM = Revolutions Per Minute
HZ = Frequency
This simple equation reveals frequency or pole count variations will significantly shift your motor's speed output.
Example:
If the motor rotor is 1200 RPM and the motor at 60 Hz, the number of poles = (120 x 60) /1200 = 6. Therefore, the number of poles for this motor is 6.
3. Physical inspection
Physical inspection is an evolution of a motor's structure, components, and overall condition. By examining the features of the motor, you can quickly determine the pole count.
3.1 Counting magnet
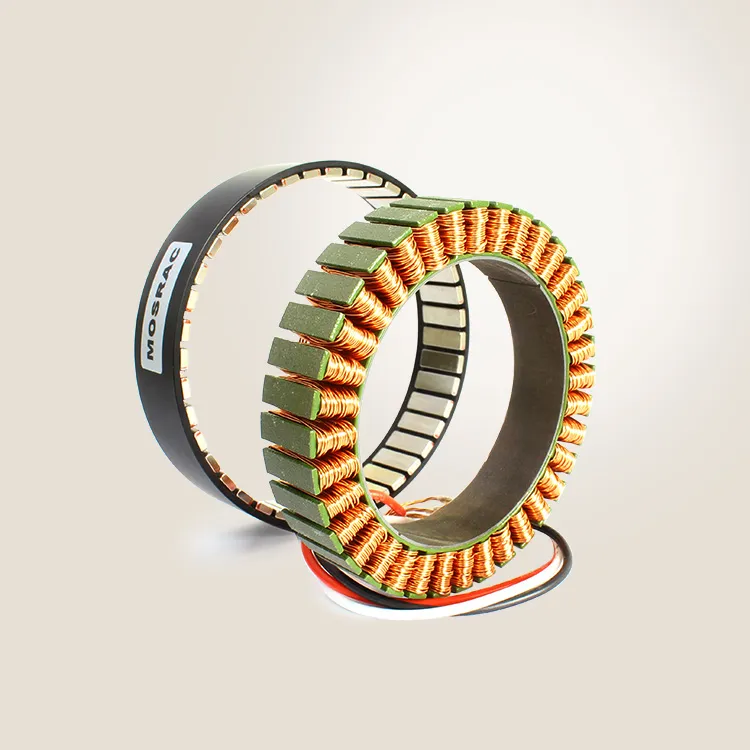
Here, the easiest way is to count the permanent magnet present in the motor’s rotor.
Number Of Motor Pole = Number Of Permanent Magnet
So, if you find two magnets, it means the pore count is 2. Likewise, by inspecting the magnets you can quickly find out the pole count. However, this technique only applies to big motors with a removable outer casing. It’s tricky to track magnets on tiny motors.
3.2 Counting motor pole pairs
Consider counting the stator windings in small motors where detecting a magnet is tricky. Each set of the stator winding represents a pole pair. You can determine the motor's pole count by observing the pole pairs.
The chart below shows you the pole pair for the different motor count and their direction:
| Motor Pole Count | Pole Direction | Pole Pair |
| 2 pole motor | 1 north magnet and 1 south magnet | 1 pole pair |
| 4 pole motor | 2 north magnet and 2 south magnet | 2 pole pair |
| 6 pole motor | 3 north magnet and 3 south magnet | 3 pole pair |
| 8 pole motor | 4 north magnets and 4 south magnets | 4 pole pair |
3.3 Reference of manufacturer documentation
The documents provide a wealth of technical specifications, including detailed wiring diagrams, torque characteristics, and operational limits. By closely examining this data, you can count poles. For instance, by naming criteria of the motor, you can identify its pole count:
| Naming Of the Motor | Pole Count |
| High-speed motors | Two poles |
| Medium-speed motors | Four poles |
| Low-speed motors | Six-poles |
| Ultra-low-speed motors | Eight poles |
4. Use motor analysis software
Motor analysis software has become invaluable for engineers and technicians, especially those optimizing motor performance. One key feature of such software is its ability to help you determine motor pole calculations, which affect efficiency, speed, and torque characteristics.
This software comes with a test stand on which you need to install the motor. The pre-written software determines the pole count of your motor while it operates at maximum speed. Simply enter the Kv of your motor into the application, and it will automatically calculate the number of poles. Within a few minutes, you will receive the final result of your motor's pole count.
How to choose the right motor pole count?
Here are the facts to consider when picking the right pole count for your motor:
1. Consider torque requirements
Torque represents the rotational strength of a motor, reflecting its ability to execute its designated task efficiently. Motors with elevated torque ratings are more effective in scenarios demanding substantial loads or quick acceleration.
For these applications, it is advisable to choose motors with a greater number of poles, as they provide enhanced torque output. Conversely, motors with low poles generate less torque and are better suited for situations where speed takes precedence over high torque.
2. Determine the desired speed
Determining the desired speed of your motor is a necessary step to selecting the correct pole count. The number of motor poles affects the speed and torque. The relationship between the pole count and the speed is inversely proportional. That is, the speed of a 2-pole motor is higher than that of an 8-pole motor.
Therefore, a motor with a higher pole count will provide a lower speed. However, choosing a high pole count can be important for applications that require high torque at low speed. So, if you want more speed, you need to prefer the lower speed pole, like 2 poles.
3. Assess cost
When choosing the correct motor polar calculation, the expense is a necessary element.
Low pole count motors will be low cost and high pole count motors will average cost high as they come with more torque. However, considering the brand and size of the motor is also crucial to determine the price.
4. Consider size and space
The physical dimensions of your application influence the motor's performance, torque characteristics, and efficiency. If you use higher poles, it means a larger rotor. Usually, larger rotter robotics cannot fit in compact spaces in machinery. So, consider the size of your machine to pick the ideal motor size.
5. Noise and vibration sensitivity
Sound and vibration sensitivity often create uncomfortable situations, significantly affecting the working environment. Extra sounds in appliances can signal the imbalance.
The high-pole motor runs smoothly and produces less noise and vibration. So, for quiet operation, motors will have more poles. For instance, a 6-pole motor operates quieter than a 2-pole motor.
6. Specific application
A higher pole count often leads to smoother operation at lower speeds and better torque characteristics, making it ideal for precision control applications.
On the other hand, a lower pole count can increase efficiency at higher speeds. This makes it suitable for industrial machinery where fast linear movement is essential.
Pros of high motor pole count
1. Increased Torque
2. Better Speed Control
3. Improved Efficiency
4. Reduced Size for Power Output
Cons of high motor pole count
1. Higher Weight
2. Complex Design
3. Limited RPM Range
4. Increased Heat Generation
Conclusion
Motor pole count is essential to optimize performance and efficiency in various applications. If you want to improve robotics projects, an accurate motor pole count is necessary to verify torque, speed, and overall performance.
Therefore, evaluate your motor's needs and consult with experts to select the ideal motor pole count for your project. Mosrac offers different types of motors. Visit our site to find the best motor for your requirements!
FAQs
1. What is the best pole count for high-speed applications?
The best pole count for high-speed applications typically ranges from 4 to 12 poles, depending on the motor's and application's specific requirements.
2. What is the most common pole count for an industrial motor?
The most common pole count for industrial motors typically ranges from 2 pole to 8 pole. However, the 2 pole 3 slot is the most prevalent choice.
3. Can I change the pole count of an existing motor?
No, the pole count is a fixed characteristic of the motor design. The number of poles in a motor is determined by its design, specifically the arrangement of coils and magnetic fields within the stator and rotor. To alter the pole count, you would need to redesign significant components of the motor, which often means constructing a new one altogether.
4. How many poles should a motor have?
The number of poles a motor should have depends on its intended application and the desired performance characteristics. In general, a motor should have a minimum of 2 poles.
Click for more information on Mosrac Motor’s direct-drive frameless motor kits.
Looking for a custom solution?
Tell us about your requirements and our application engineers will help you find the right solution today!
Any questions or comments about Frameless Motors, Direct Drive Rotary Motors, and Encoders? Contact us at sales12@mosrac.com for sales, technical inquiries, or order samples online today!