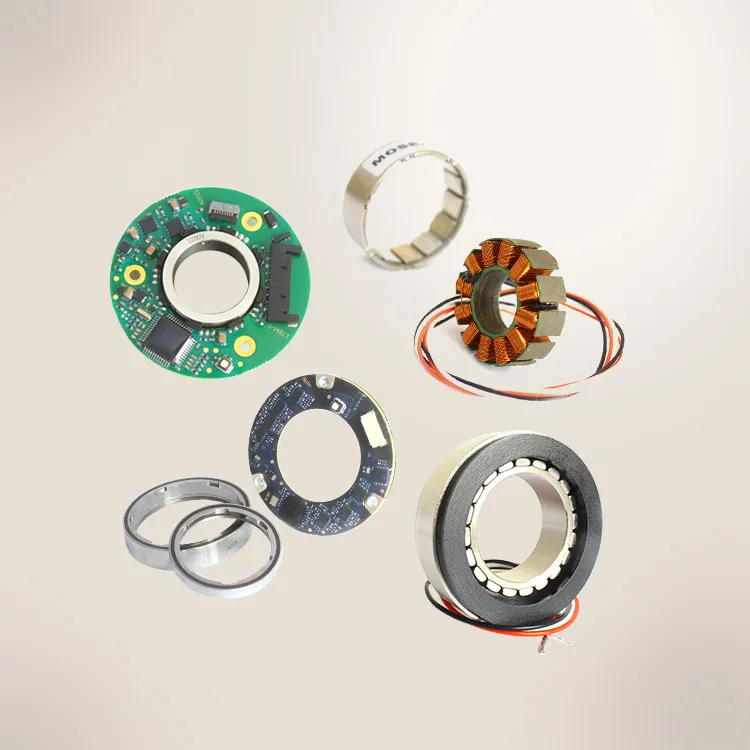
Introduction:
Choosing the right torque motor is quite important to ensure enhanced performance and energy efficiency in industry applications. The right choice of torque motor relates to matching the motor’s capacities for the application's specific requirements. Choosing the right torque motor can be a complex task, but it can be easier if you follow some important criteria to choose the right one.
Some of the important factors need to be considered for choosing the right torque motor to ensure excellent system performance. Choosing the right torque motor involves considering factors, such as load characteristics, horsepower requirements, inertia during the startup, duty cycle, environmental conditions, and energy-saving requirements. Making an informed decision is crucial to selecting a torque motor for use to ensure optimal performance.
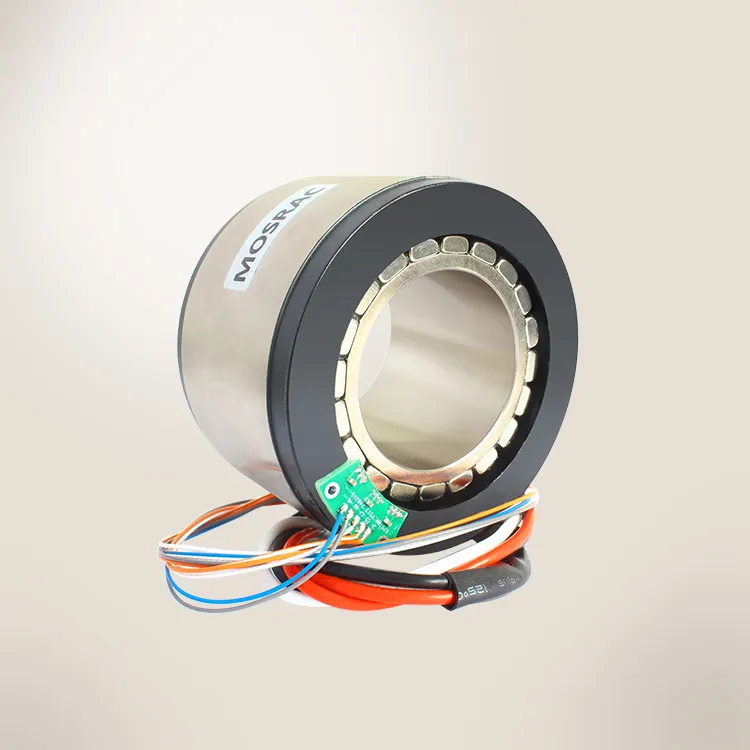
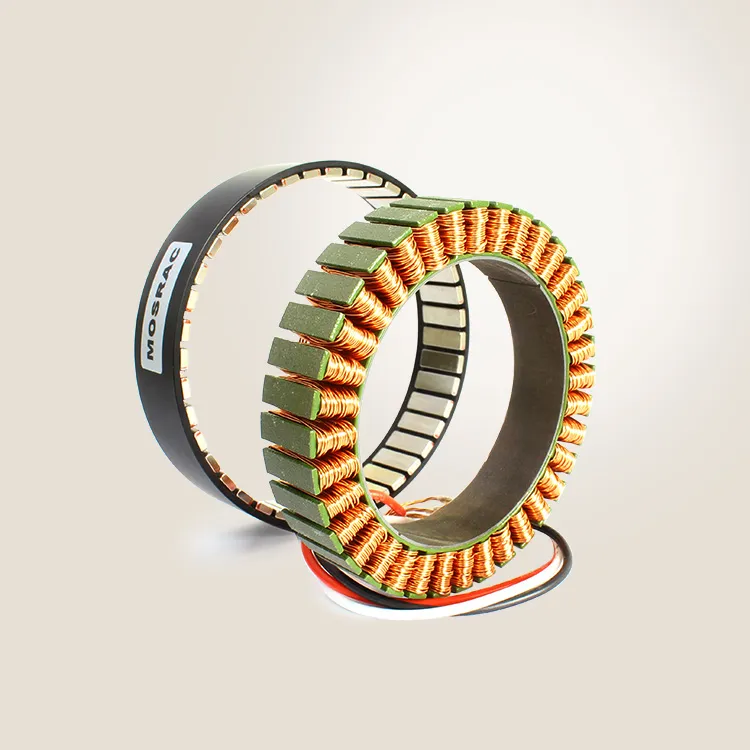
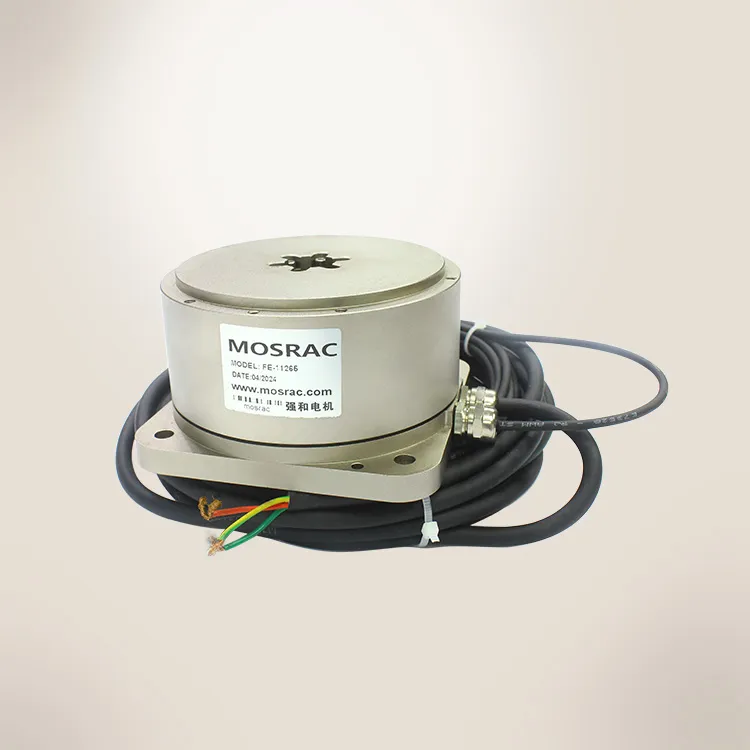
MOSRAC has high-quality frameless torque motors with exceptional design and performance for robots. These torque motors are appropriate because of their higher reliability, fast speed, cost-effectiveness, acceleration, and accurate positioning for various applications.
In this article, we will discuss and highlight the key considerations for choosing an appropriate torque motor. This comprehensive overview will help you make an informed decision for choosing the right torque motor.
Significance of choosing the right torque motor:
A: Compatibility with the system:
The right torque motor provides accurate speed and torque for the system and will have a significant impact on the c12.ompatibility of the system. The important parameters of the torque motor, such as voltage, current, and frequency, play a vital role in the system.
The torque motor that is not compatible with the system will cause lower performance and efficiency and damage to the system.
B: Control capabilities:
The right torque motor, along with its speed control, torque control, and position control, will have a big impact on the system to meet the system's application.
C: Energy efficiency:
The energy efficiency of the right torque motor plays a significant role in operating at high levels of efficiency across a range of loads. This can help in minimizing power consumption and costs.
D: Efficiency:
Torque motors may vary in terms of efficiency, which can have a significant impact on both operating costs and environmental impact. Choosing the right torque motor to meet the required standards for system efficiency is always important. Some important considerations are:
▪︎ Specific efficiency requirements:
The specific efficiency requirements of the system need to be determined for better system application before selecting the right torque motor.
▪︎ High efficiency rating:
Torque motors with high-efficiency ratings can save energy and reduce operating costs.
▪︎ Load factor:
It is always important to consider the load factor before choosing the right torque motor. The torque motors that are oversized or undersized for the application can lead to reduced efficiency and increased energy costs.
The load factor of a motor defines as the ratio of its average load to its highest demand. Load factor is the amount of how a motor uses electrical energy efficiently.
A high load factor defines the motor is using the electric system effectively and a low load factor shows the motor is underutilizing the electric distribution. For example, if a 10-horsepower motor operates at 6-horsepower load and runs 50% of the time, its load factor is 60%. The equation for the load factor is:
Load Factor = Average Load / Maximum Demand Over Specific Time of Period.
The value of load factor is required to be less than one since the average load is less than the highest demand. Improving load factor relates to minimizing peak load requirement. It increases the value of the load factor, saves electrical energy, and minimizes the average cost per unit. A low load factor shows high maximum demand and low utilization rate.
▪︎ Proper installation and maintenance:
Proper installation and maintenance of the right torque motor plays an important role in ensuring high efficiency. Checking accurate alignment and tension of belts, and replacing worn or damaged parts regularly, are important parts of proper installation and maintenance.
14 Essential Criteria for Choosing the Right Torque Motor:
1. Higher Power Density:
Power density is the amount of power produced by the motor based on its size and weight. High power density relates to high-torque techniques that take up minimum space. High efficiency, high dynamics, and high power density are the three most important issues for motors used in robotic applications. A motor with a higher power density is favored for a more integrated and lightweight design. Major robotics applications will require high motor power density with high torque capacity.
2. Low Detent Torque Effect:
A motor’s detent torque is the amount of torque generated by the motor when the windings do not get energized. This type of torque becomes available when there is no current in the motor coils. If there is a torque without excitation, a fixed magnet can generate the detent torque by a fixed magnet because of its magnetism. Most types of motors have detent torque.
The detent torque is required to overcome the magnetic resistance to make the motor move. More power from the motor is required to overcome the detent torque, and the amount of required power is proportional to speed. If the motor runs fast, the effect of the detent torque will be high on the motor’s actual torque output. It minimizes the real torque that the motor can generate when it’s running. It is very important to have very low detent effects for torque motors.
3. Higher Motor Constant:
The motor constant, Km, is the connection between torque generated and power dissipation. The inner design of the motor uses this parameter. It shows the motor performance more than the torque constant. A motor with a higher value of Km is a more effective producer of torque. Robotic joints have a huge application of Km. The value of the motor constant is important for sizing motors for applications like heat dissipation and motor surface issues in humanoid robots.
4. Longer Duty Cycle:
The duty cycle plays a vital role in the selection of a torque motor. A low-power motor should choose a load that needs a low-duty cycle. A motor with a higher-duty cycle is necessary for a higher run time.
There are two types of duty cycles, such as continuous duty or intermittent duty. Continuous duty relates to a long time of stable operation and intermittent duty shows frequent startups and rushes of heat. The duty cycle needs to be evaluated carefully so that the motor can manage the specific requirements of the application. The environmental temperature can affect a motor’s duty cycle.
The duty cycle of a motor defines as the proportion of on time and off time and shown as a percentage. It explains the frequency and time of operations, like starting, running, electric braking, and resting. It is important to choose a motor for a suitable application. There are some key factors that can affect the duty cycle of a motor, such as load, voltage, and temperature.
There are four types of motor duty cycles, such as:
Continuous Duty Cycle: The simplest type of cycle is a continuous duty cycle. The motor operates with a fixed load for a long time to attain thermal equilibrium in this type of operation. The advantages include efficiency, dependability, and simplicity.
Short Time Duty Cycle: The second type of operating cycle is a short time. This operation operates with a fixed load. It shuts off before it reaches thermal equilibrium.
Intermittent Periodic Duty Cycle: Intermittent periodic duty is the simplest type of variable duty. This type of duty cycle contains a period of constant load and a period of rest.
Perpetual Operation with Electric Braking: This type of duty cycle is a continuous operation with electric braking that has a starting sequence, fixed load, and electric braking.
5. Reduced Thermal Expansion:
Torque motors produce heat during their operation. This type of heat needs to be removed to minimize the thermal expansion of the torque motor. It is important to keep the torque motor cool for its high precision. Thermal management is important for direct drive applications.
6. Improved Inertia Matching:
The properties of inertia need to be assessed to select a torque motor. Inertia matching is defined as the matching of load inertia and motor inertia. A low load-to-motor inertia ratio is essential for high acceleration and accurate positioning to attain the desired outcome in the applications.
The harmful effects of inertia mismatch can be high because of the lack of stiffness in the system which causes higher response times, lower system bandwidth, and resonance. It will be difficult to get acceleration if a system has a high rotational inertia. If the system has smaller rotational inertia, then it will be easier to get acceleration.
7. Motor Size:
The physical space of a torque motor is an important matter for consideration. The size and capacity of a torque motor will affect operational efficiency. There are different sizes of torque motors with compact designs. Choosing a torque motor fitting within the optimum space and meeting the weight or vibration issues is an important matter.
8. Maximum Speed:
A torque motor needs to deliver constant speed for the operation of the motor. The torque motor operates at a stable speed throughout its range of motion for accurate movements.
The zero torque point on the torque-speed curve chooses the highest speed of a motor. The speed of the motors will control the robot’s motion functions. Industrial robotic arms usually need high-speed capabilities.
9. Suitable Torque:
Choosing the right torque motor relates to finding out the torque to calculate the expected power. The torque motor requires a definite torque and speed to cause a movement for a specific application.
▪︎ Starting Torque:
The starting torque, torque at zero speed, is the torque that the motor can deliver if rotation begins. The motor requires generating the torque enough to surpass the friction and load torques for a self-starting system. The variation between the motor torque and load torque creates the acceleration of the system. If the motor torque is like the load torque, the steady state operating speed happens.
▪︎ Torque-Speed Variations:
Choosing a torque motor with similar torque-speed properties is important when the load line exists. A load line delivers the torque-speed relation appropriately. In this situation, the torque of the motor and load will be similar over a large range of speeds. The small modifications in voltage to the motor can regulate the speed. The zero torque point on the torque-speed curve chooses the highest speed of a motor.
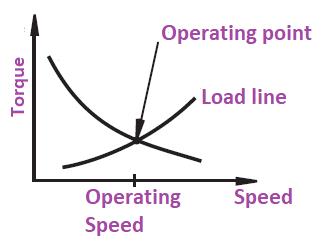
Figure 1: Motor torque-speed curve
10. Higher Reliability:
Reliability is a critical matter in choosing a torque motor. The design of the torque motor should be appropriate so that it can function consistently and reliably with reduced maintenance.
11. Low Cost:
Torque motors need to be cost-effective because they don’t need mechanical transmissions like gearboxes, belts, and speed reducers. This reduces maintenance costs. The price of a torque motor relies on the parts and materials used, as well as the motor's performance capacities.
12. Optimum Load Power:
An electric motor changes electrical energy into mechanical energy based on a mechanical burden. Some variables, such as power, voltage, current, and temperature, assess the motor. If the load increases on the motor, then it will draw more power from the source and higher current flowing to the motor. As most of the power supplies are voltage sources, motors will take more current for the increased load.
▪︎ Variable Torque Load:
Variable torque loads need lower torque at low speeds than at high speeds. The torque changes with the square of the speed and the horsepower changes with the value of the cube of the speed.
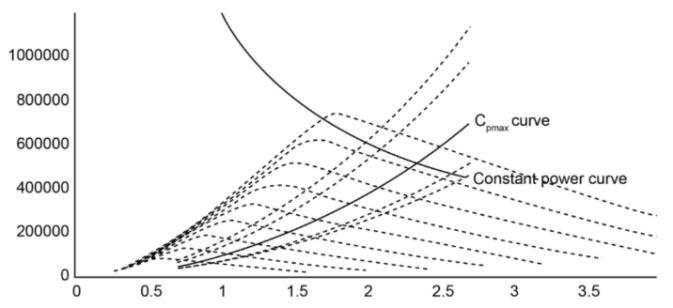
Figure 2: Variable Torque Load
▪︎ Constant Torque Load:
Constant torque loads need the same measurement of force at low and high speeds. Force remains stable through the speed range and the torque increases and decreases in direct proportion to the speed.
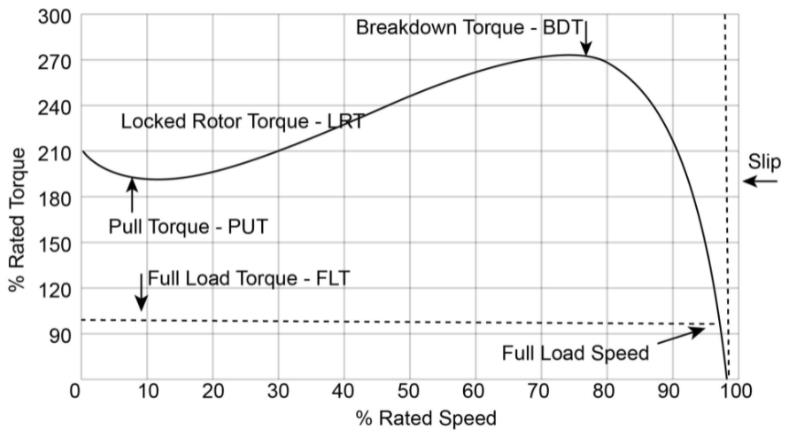
Figure 3: Constant Torque Load
▪︎ Constant Power Load:
Constant power load needs high force at low speeds and low force at high speeds and shows stable strength at any speed. Stable strength loads include processors, winding machines, and machines.
13. Production Environment:
The environment plays a significant role in the operation of a torque motor on its performance and longevity. Choosing the right torque motor relates to some issues, such as temperature and medium. For example, motors used in harsh or corrosive environments may need coatings to prevent destruction. Motors used in high-temperature environments may need cooling methods.
14. Motor Reversibility:
Some motors are not reversible because of their construction and control electronics. It is important to choose a motor for the applications of rotation in two directions.
How MOSRAC will help you find the right torque motor?
1. Innovative Research and Development:
MOSRAC has extensive and innovative research and development experience in torque motor design and manufacturing. It concentrates mainly on the advancement of direct drive technology, the torque motor. We are ready to help you provide unmatched torque efficiency for the most optimized performance.
2. Higher Application Requirements:
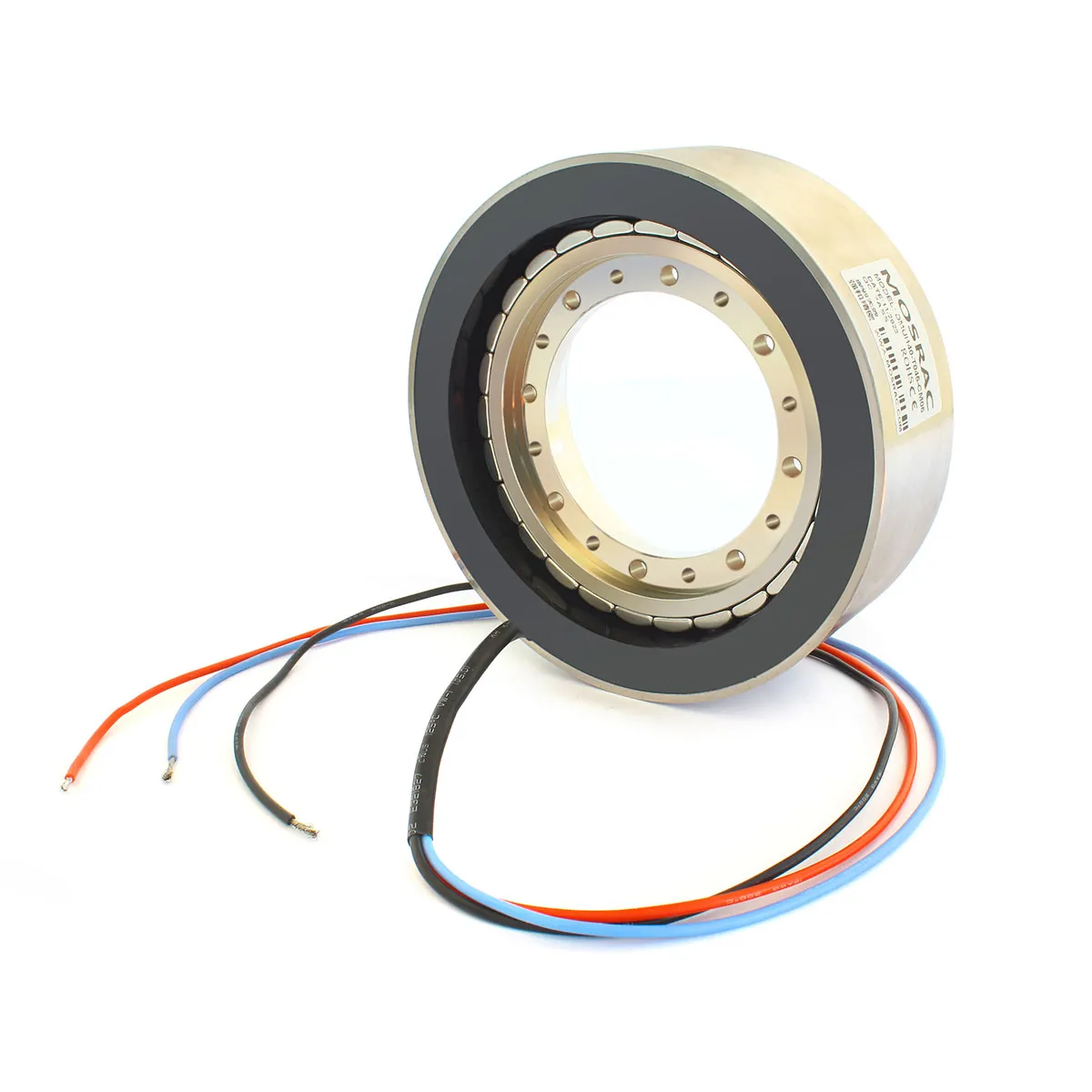
MOSRAC provides torque motors with ranges of voltages from 24 to 48V and outer diameters from 25 to 200mm. Our torque motors meet current standards and have the quality for use in any production environment.

Figure 4: MOSRAC Frameless Torque Motor
3. Higher Advantages:
MOSRAC offers a very compact design, high precision, higher overload capacity, high torque density, and lightweight torque motors. These are appropriate for robotics, medical, automation, and aerospace industries.
4. Excellent Custom-Oriented:
MOSRAC torque motors help attain excellent torque, speed, size, and temperature for many applications. We commit to providing our customers with the best possible solutions for choosing a torque motor that best suits their application. MOSRAC is prominent and recognized for its advancement of special and fully customized torque motors.
5. Low Detent Torque Effect:
MOSRAC design of torque motors minimizes detent effects significantly for higher torque density.
6. Reduced Thermal Expansion:
MOSRAC torque motors deliver advanced cooling channel design for higher heat evacuation through the coolant. MOSRAC torque motors generate much more torque for the same input power than competitive products because of their improved electromagnetic design.
Conclusion:
Choosing the right torque motor for application provides increased productivity, reduced energy consumption, and overall cost savings. With the knowledge and insights, the chosen motor aligns perfectly with specific requirements. Choosing the right torque motor for application is crucial to attain optimal performance and efficiency. When choosing a torque motor, it is important to consider various factors, including control capabilities, power, torque, speed, and acceleration requirements of an application for optimal performance.
Maximum adaptability, compact size, lightweight, excellent torque, higher speed, and optimum size are the key factors of MOSRAC frameless direct-drive torque motors. MOSRAC commits for its advancement of special and fully customized torque motors. Its torque motors attain industry-customized performance and are cost-effective. Got a question about torque motors? Contact me by email.
Looking for a custom solution?
Tell us about your requirements and our application engineers will help you find the right solution today!
Any questions or comments about Frameless Motors, Direct Drive Rotary Motors, and Encoders? Contact us at sales12@mosrac.com for sales, technical inquiries, or order samples online today!